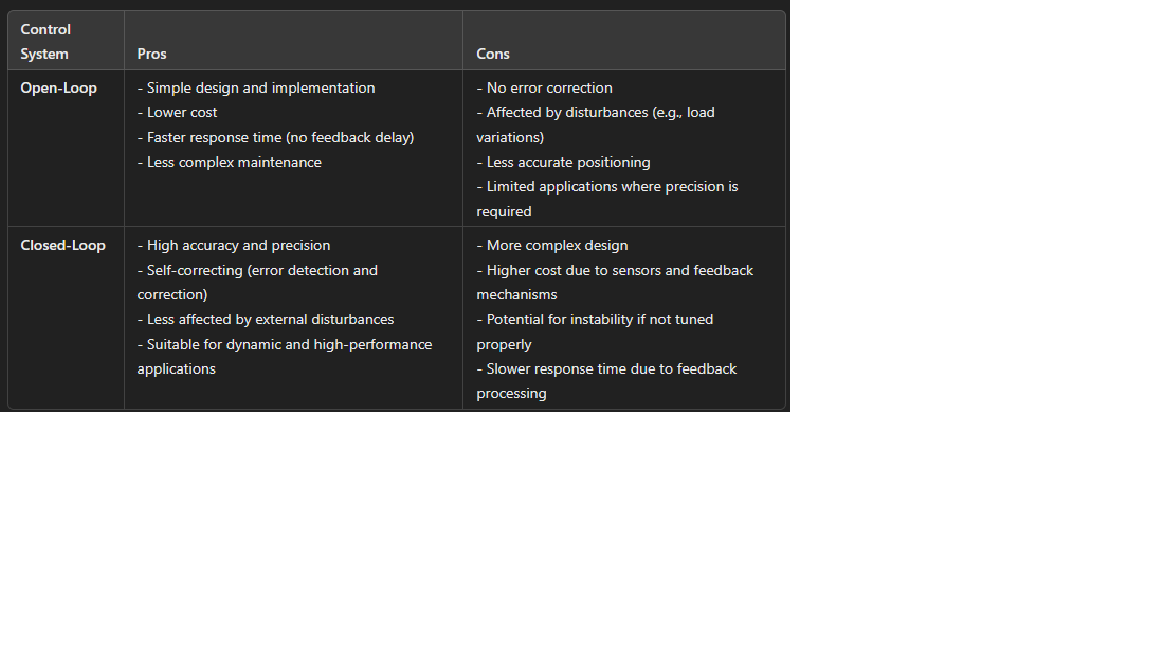
Servo motors are a crucial component in automation, robotics, and various control systems. They are designed for precision control of angular or linear position, velocity, and acceleration. There are three basic types of servo motors: positional rotation motors, continuous rotation motors, and linear motors. Each type has unique characteristics, advantages, and specific applications.
Read more: Three Basic Types of Servo MotorsPositional Rotation Servo Motors
Specifically designed for limited-angle rotation; positional rotation motors usually rotate between 0 and 180 degrees. They contain built-in feedback mechanisms, typically using a potentiometer, to control precise positioning.
Characteristics & Applications
- Less than 180 degree rotational movement.
- Used for precise angle adjustments
- Compact and cost effective
- Commonly used in camera gimbals, robotic arms, and small automated systems.
Continuous Rotation Servo Motors
Continuous rotation motors are designed to rotate continuously in either direction, similar to a DC motor but with controllable speed and direction. These do not have position feedback but instead rely on pulse width modulation (PWM) signals to control their speed and direction.
Characteristics & Applications
- Has full 360 degree rotational movement in either direction.
- Speed and direction controlled via PWM signals.
- No built-in position feedback
- Used in processes that require continuous movement such as conveyor belts and motorized platforms.
Linear Servo Motors
Linear motors convert rotational motion into linear motion, providing precise control over movement in a straight line. These motors are commonly used in applications that require accurate positioning along a linear path.
Characteristics & Applications
- Can convert rotational motion into linear motion
- Very precise and accurate
- Incorporates lead screws, belt drives, and directional actuators
- Used in operations that require linear movement such as CNC machines and 3D printers.

Conclusion
Each type of motor serves different applications based on its characteristics and advantages. Positional rotation motors offer precise control for limited-angle movements. Continuous rotation motors provide controllable speed and direction for continuous movement. Finally, linear motors enable precise linear motion control. Understanding these differences helps in selecting the right servo motor for any given application, ensuring efficiency and accuracy in motion control systems.
Other Articles
If you have found what you have read helpful then check out our article on extending your servo motor life. Feel free to also check out our article about the warning signs of a failing servo motor.
Looking for a parts?
Are you in the market for a servo motor? Let our team of experts help you get set up!