Factory Automation and Machine-to-Machine (M2M) Advances
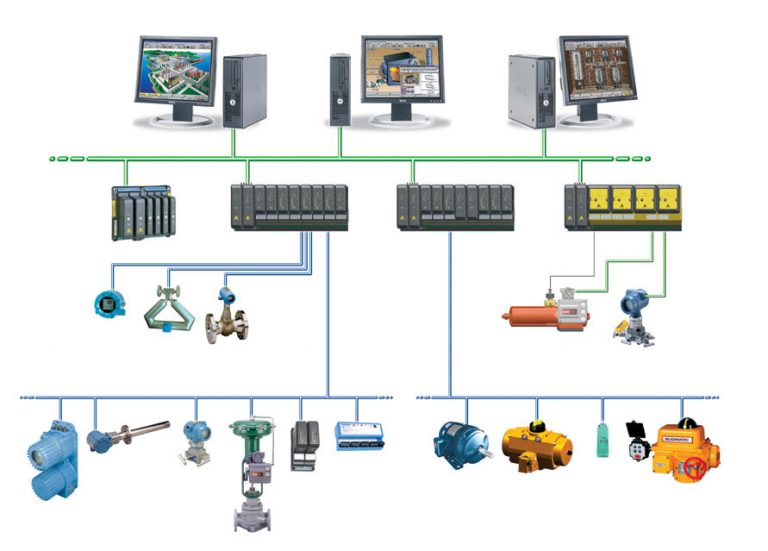
As technology evolves, automation has become more and more prevalent in the factory automation space. Machine-to-machine enables private and exclusive communication and control over sensors, cameras, industrial equipment, robotics (check out our FANUC Robotics parts) and essentially anything else. Manufactory facilities and several other remote systems are managed much more easily with machine-to-machine advances in communication.
Initially, with industrial and enterprise applications as a focal point, machine-to-machine communication was easily defined and used for a limited amount of tasks. Nowadays, there are many fewer limitations associated with the machine-to-machine communication.
Pressured to lower costs and improve speed and overall efficiency, factory automation companies are often in an uncomfortable spot. While using high-end, sophisticated automation applications and tools, more real-time data must be obtained to streamline more of the day-to-day operations and tasks. Implementing machine-to-machine solutions can help with operational efficiency gains, time and cost savings, and performance optimization.
From a cellular standpoint, machine-to-machine solutions enable integration of environmental controls into a single system, and to unify with security and video surveillance systems. All and all, companies are able to secure several properties from anywhere they wish to, even as they fine-tune power efficiency and decrease operating expenses.
Due to the immense increase of machine-operated plants in companies who rely on keeping critical assets and functions performing optimally, several companies are exploring options associated with a machine-to-machine communication. Of the many benefits, the fact that it’s able to deliver remote access to gather real-time process data to cut operation costs is often one of the most well-recognized. The ability to identify and rectify production line faults, or design and implement preventative maintenance strategies, for example, is what machine-to-machine communication is designed for.
Involving data exchange over the telephone line or via the internal with machines, plants, computers for issue detection, diagnostics, and repair, teleservice is an imperative aspect of machine-to-machine communication. Offering an optimal answer to diagnose distant systems, teleservice is becoming more and more popular and is not going anywhere.
Telecontrol, another aspect of machine-to-machine communication, deals with connections of distant process stations to one or more central control systems. Many networks, both public and private, can be used for communication used to control. For these diverse applications and businesses, cellular M2M connectivity can address many business and technical challenges and enable important benefits.
MRO Electric and Supply has new and refurbished FANUC parts available. We also offer repair pricing. For more information, please call 800-691-8511 or email sales@mroelectric.com.
Additionally, M2M systems can be designed to withstand harsh environmental conditions and easily manage and control connected devices across the country or around the world. M2M systems provide flexibility to move equipment as needed, or bring up and tear down systems quickly for temporary or seasonal deployments. By using modern M2M management and application platforms, and taking care to choose platforms designed to meet real-world requirements, organizations can take full advantage of the M2M revolution.
In case you were wondering, machine-to-machine systems are indeed designed to withstand environmental conditions and easily control connected devices in any location. They are flexible and can move equipment with ease. In order to use machine-to-machine communication optimally, look into management and application platforms. Click here to view our article on IT and Robotics.